Rockets are powerful machines that utilizes thrust generated by the propulsion systems to propel itself through space. The thrust is obtained by high speed exhaust gases created by burning fuel with oxygen in appropriate ratios. The rockets work on the principle of Newton’s third law of motion which is “Every Force has an equal and opposite reaction.” These man-made marvel have played a crucial role in space exploration, satellite deployment, scientific research and even transportation.
History of rockets
The history of rockets dates back thousands of years in the ancient China homeland using solid propellants. With modern developments starting in the 20th century only possible with advancements in chemical knowledge, physics and engineering. Today rockets come in various sizes and configurations for specific requirements which can propel payloads into orbits and beyond, helping us explore the space and aiding in launching of the satellites into its orbits.
The basic components of a typical rocket include a propulsion system, a guidance and control system, a structure or air-frame, and a payload or cargo. Let us explore these components further:
Propulsion System
The propulsion system generates necessary thrust required to launch the rocket into the space which can only be done by creating a force greater than the Earth’s gravitational pull. It consists of one or more than one rocket engines that burn propellants, these propellants can be in the solid and liquid form, to produce a very high velocity exhaust. These hot exhaust gases are expelled through a nozzle located at the rear end of the rocket at a very high speed, which helps in creating a forward force called thrust.
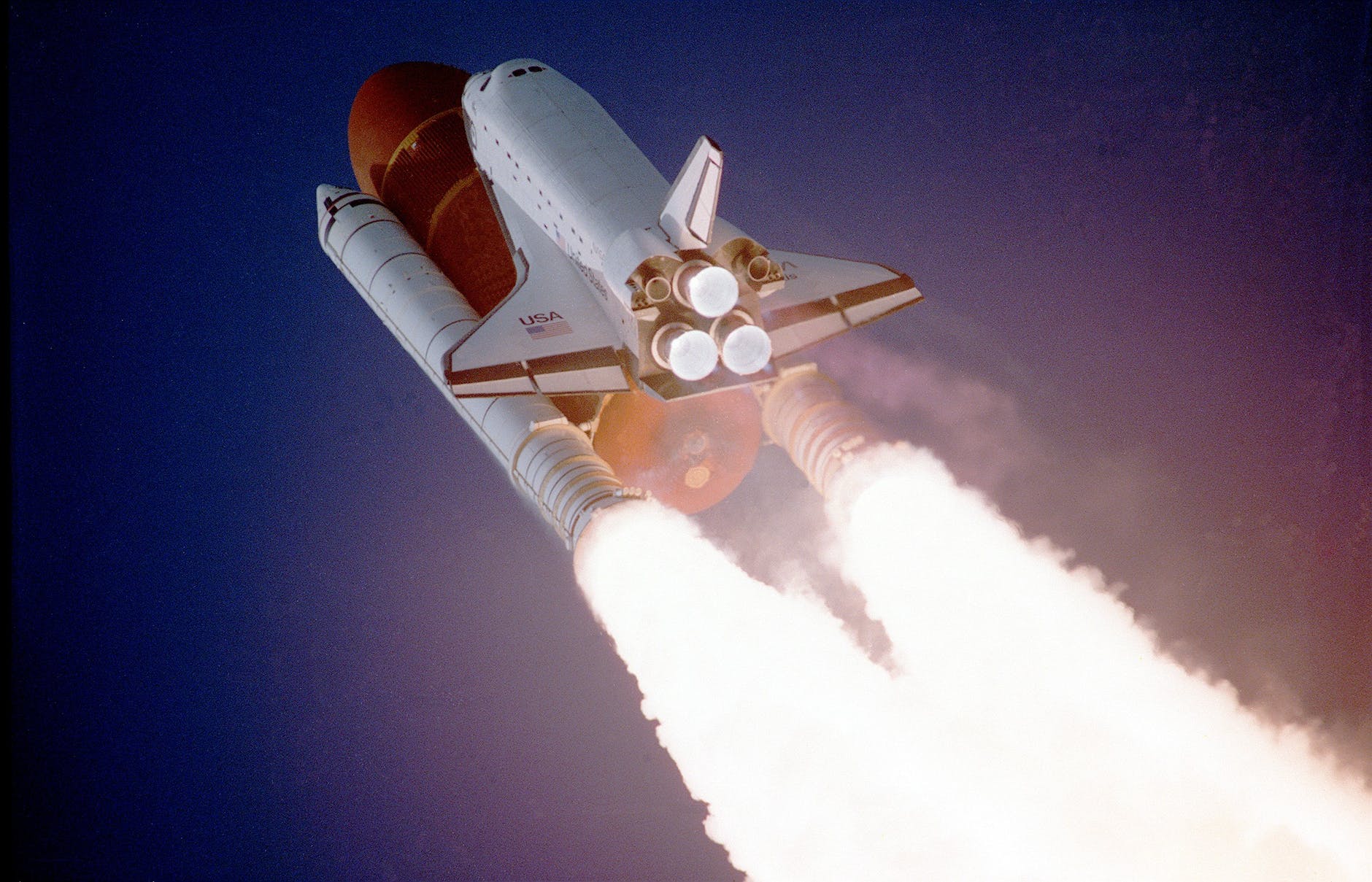

Rocket propulsion system
Guidance and Control System
In order to reach their intended destination rockets needs precise control and guidance systems. The guidance and control system includes sensors, namely the gyroscopes and accelerometers. The data obtained by these sensors are analysed by the onboard computers and software algorithms and necessary adjustments are carried out to the rocket’s trajectory. This complete system ensures stability, accuracy and the ability to corrects any deviations during flight. Most modern and more advanced rocket systems utilizes vision sensors in the form of cameras and radars which can help rockets to alter its path in case there is obstruction in its trajectory to avoid collision and damage.

Rocket guidance and control systems
Structure or Airframe
The structure of a rocket provides support and houses all the components. It is designed to withstand the immense forces experienced during launch and flight. Rockets are typically cylindrical in shape, with a streamlined nose cone at the front to reduce aerodynamic drag. The air-frame is often made of lightweight materials, such as aluminum alloys or composites, to maximize payload capacity while maintaining structural integrity.
Rocket structure and airframe
Payload or Cargo
The payload refers to the cargo carried by the rocket. It can vary depending on the mission objectives and can include satellites, scientific instruments, spacecraft, crewed capsules, or even supplies for space stations. The payload is typically located at the top of the rocket and is protected by a fairing or shroud during the initial phases of flight.

Rocket carrying payload cargo
How do rockets fly?
Rockets operate based on Newton’s third law of motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. As propellant is expelled at high speeds from the rocket’s engines, it generates an equal and opposite force that propels the rocket forward.
Modern rocketry has enabled us to explore the vastness of space, launch satellites into orbit for communication and observation purposes, conduct scientific experiments in microgravity, and even send humans to the Moon and beyond. Rockets continue to be at the forefront of space exploration, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and paving the way for future advancements in technology and our understanding of the universe.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe our Youtube Channel.


Thank you for writing this article. I appreciate the subject too.
How can I find out more about it?
Thank you for your articles. They are very helpful to me. May I ask you a question?
The articles you write help me a lot and I like the topic
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!